
In the previous chapter, we looked at angular momentum. Remember the "Dizzy Physics Professor" scenario?
Now we will extend those ideas and look at the vector nature of angular momentum.
Angular Momentum - 2
L = I 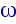
The angular velocity ![]() and the angular momentum L are both vectors! The
vector lies along the axis of rotation and points toward one end
or the other according to the "right hand rule":
and the angular momentum L are both vectors! The
vector lies along the axis of rotation and points toward one end
or the other according to the "right hand rule":

Rght Hand Rule

Just as we wrote
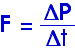
for the linear case, we can also write

for the rotational equivalent.
Remember, torque is a vector. When we wrote
or
![]()
r and F are vectors and their "cross product" or "vector product" is also a vector!
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|||