

Circular Motion
Nonuniform Circular Motion
Any object moving in a circle -- or just a part of a circle -- has a centripetal acceleration, directed toward the center of that circle. That means it has a centripetal force acting on it, also directed toward the center of that circle. "Directed toward the center" can also be stated as "radially". That is, any object moving in a circle -- or just a part of a circle -- has a radial acceleration. That means it has a radial force acting on it.
In addition, the object may be accelerating tangentially -- along the direction tangential to the circle or perpendicular to the radius. If this is the case, then there is also a tangential force or the net force has a tangential component as well as the radial component.
The total or net acceleration is the vector sum of the radial and tangential components. Likewise, the total or net force is the vector sum of the radial and tangential components.
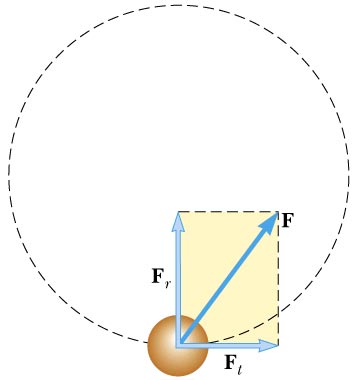


Table of Contents (c) Doug Davis, 2001; all rights reserved