|
|

|
|

Electromagnetic radiation with longer wavelengths is called infra-red radiation and is often referred to simply as IR radiation. Our eyes can not detect this IR radiation but our skin feels it as heat. Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than the visible range is called ultra-violet radiation and is often shortened to UV radiation. Again, our eyes can not detect this UV radiation but its effects are real. UV radiation causes sunburns and suntans; UV radiation can also cause skin cancer and eye damage. Electromagnetic radiation is often abbreviated and people will talk of EM radiation or EM waves.
When we talk of the photoelectric effect in our study of Modern Physics, we will find that the energy contained in a photon, a "packet" of light, depends upon the frequency or the wavelength. Ultraviolet light has the shortest wavelength and that means each UV photon carries more energy than a visible light photon. That is why UV photons are able to do more damage than visible light photons.
The phrase "visible light" may be considered redundant. "Light" means EM waves that can be detected by our eyes, or EM waves that are visible. It is entirely proper to limit use of the word "light" to the visible range from 400 nm to 700 nm in wavelength. In common usage, however, people often extend the use of "light" to include infra-red and ultra-violet as well. Thus, both "UV light" and "UV radiation" are commonly heard and both are easily understood.
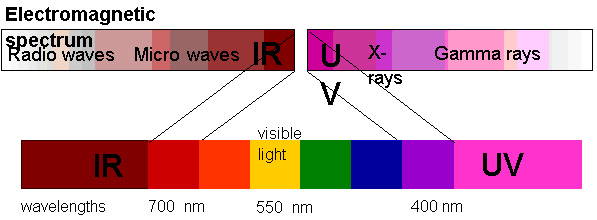
A: Radio waves and light are, indeed, similar. Both are electromagnetic waves and radio waves do have longer wavelengths than light.

|
|