

Ch 8: Rotational Motion; Ex 13, 18, 23, 24, 28, 29, 31, 32, 34, 49; Pb 3, 5
![]()
Ex 8.13 When a car accelerates forward, why does its front end rise? Why does its front end dip when braking?
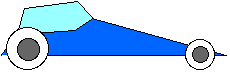
A car accelerates -- forward when moving faster and faster or backward when braking -- because of the forces supplied to its wheels by the highway. Look at the rotational effect of these forces (that is, look at the torques caused by these forces). Take these torques about the center of mass.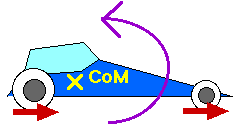
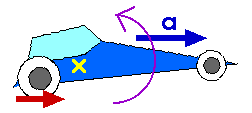
When a car accelerates forward, the highway exerts a force forward on the wheels. This forward force causes a counterclockwise torque. That is, in addition to causing the forward acceleration, this torque -- this rotational effect of the force -- will cause the car to rotate counterclockwise. A counterclockwise rotation means the nose will rise.
Of course the nose can rise enough that it looses contact with the road; that is referred to as a "wheelie". You can see this done with bicycles as well.
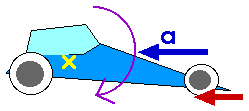
When a car accelerates backward -- as in braking -- the highway exerts a force backward on the wheels. This forward force causes a clockwise torque. That is, in addition to causing the backward acceleration, this torque -- this rotational effect of the force -- will cause the car to rotate clockwise. A clockwise rotation means the nose will dip.
"Clockwise" and "counterclockwise" depend upon "forward" being "to the right" and "backward" being "to the left" as shown in these diagrams.
Ex 8.18 Is the net torque changed when a partner on a seesaw or teter-totter stands or hangs from her end instead of sitting? (Does the weight or the lever arm change?
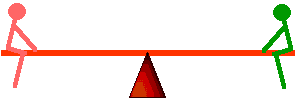
In every case, the weight is straight down. The moment arm (or lever arm) is the perpendicular distance from the pivot to the weight. This means the counterclockwise rotational effect of the force (that is, the torque) is the same whether the partner sits, stands, or hangs from the seesaw or teeter-totter.
Ex 8.23 Why is the wobbly motion of a single star an indication that the star has a planet or system of planets?
The center of mass does not wobble. So if we see a single star that wobbles, that means that something else -- which we may not see -- is also wobbling to keep the center of mass stationary. The "something else" could be planet or a system of planets or another star that we are unable to see.
Ex 8.24 Why must you bend forward when carrying a heavy load on your back?
You have to keep the center of mass above your feet -- your area of support.
Ex 8.28 Sometimes a kicked football sails through the air without rotating, and at other times it tumbles end over end as it travels. With respect to the center of mass of the ball, how is it kicked in both cases?
For the tumbling situation, the football is kicked with a torque about its center of mass. It is kicked so the force has a considerable rotational effect.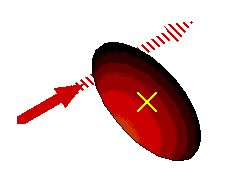
For the non-rotating case, the football is kicked so the force is directed at the center of mass. That kick provides no rotational effect.

Ex 8.29 How can the three bricks shown below be stacked so that the top brick has a maximum horizontal displacement from the bottom brick? For example, stacking them like the dotted lines suggest would be unstable and the bricks would topple. (Hint: Start with the top brick and work down. At every interface the center of gravity of the bricks above must not extend beyond the end of the supporting brick.)
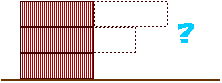
Using the Hint, let's start with the top two bricks. The topmost brick can be positioned with its center of mass just on the edge of the second brick.
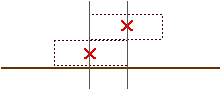
Where is the center of mass of this two-brick system? The center of mass is the "average position" of the masses, so it must be mid-way between the centers of mass of the two bricks,
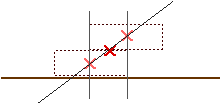
The center of mass of this two-brick system is located at a distance of 3/4 of the length of a brick from the left end of the bottom brick, as shown above. We can now put this on top of the bottom brick so tha this center of mass is just over the edge of the bottom brick,
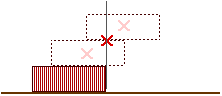
With this arrangement, the topmost brick can be extened 3/4 of the length of a brick beyond the bottom brick.
Ex 8.31 Why is it dangerous to roll open the top drawers of a fully loaded file cabinet that is not secured to the floor.
Remember, to be stable, the center of mass must be above the area of support. Rolling open the fully loaded drawers of a file cabinet can move the center of mass out, beyond the base of the file cabinet. This would cause it to tip over.
Ex 8.32 Describe the comparative stabilities of the three objects shown in Figure 8.31, on page 135, in terms of work and potential energy.
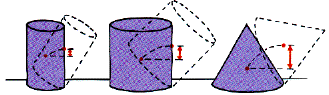
When each one is tipped, its center of mass is raised. This means each one is now sitting in stable equilibrium. Going from left to right, as each one is tipped, its center of mass or center of gravity is raised more than the one to its left. That means more work is done to tip each succeeding one. That means each one is more stable than the one on its left.
Ex 8.34 A long track balanced like a seesaw supports a golf ball and a more massive billiard ball with a compressed spring between the two. When the spring is released, the balls move away from each other. Does the track tip clockwise, tip counterclockwise, or remain in balance as the balls roll outward? What principles do you use for your explanation?
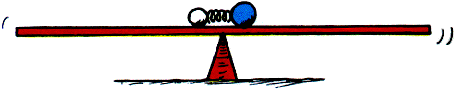
The center of mass is initially located directly above the pivot. When the two balls spring apart from each other, they do so in a manner that leaves the center of mass where it was. That is, after they spring apart, the center of mass remains directly above the pivot. Therefore, the track remains balanced!
Ex 8.49 Why does a typical small helicopter with a single main rotor have a second small rotor on its tail? Describe the consequence if the small rotor fails in flight?
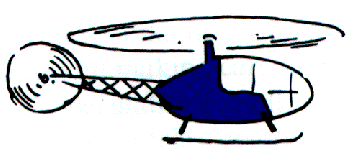
The small rotor exerts a force at the end of a long lever arm. This provides a "rotational force" on the helicopter to oppose or counteract the "rotational force" supplied by the main rotor. Consider a helicopter initially at rest. As the main rotor starts and gains angular momentum, the body must have a "rotational force" on it or it will start rotating in the opposite direction so that it has angular momentum in the other direction. The small tail rotor supplies a "rotational force" so the body does not rotate.Russian helicopters usually have counter-rotating main rotors on top so that the angular momentum of the two main rotors is zero.
Ex 8.** Which will roll down a hill faster -- a solid cylinder or a solid sphere?
From Figure 8.3, on page 117, we know the "rotational mass" or "moment of inertia" for a solid cylinder to be I = (1/2) m r2 and for a solid sphere to be I = (2/5) m r2. With its smaller "rotational mass", the solid sphere is easier to rotate so the solid sphere will roll down a hill faster.
Ex 8.** Which will roll down a hill faster -- a solid ball or a hollow ball?
From Figure 8.3, on page 117, we know the "rotational mass" or "moment of inertia" for a hollow cylinder or ring or hoop is I = m r2 and for a solid cylinder or disk is I = (1/2) m r2. The hollow cylinder or ring or hoop has all its mass a a distance r away from its axis of rotation. The solid cylinder, however, has its mass distributed throughout. Some of its mass is even on the axis of rotation. This means the "rotational mass" of the solid cylinder is smaller.Figure 8.3 does not give us the "rotational mass" of a hollow sphere or a hollow ball. However, we can still know that the "rotational mass" of a solid sphere will be smaller than the "rotational mass" of the hollow sphere. This is because the solid sphere will have more of its mass at a smaller distance from the axis of rotation.
With its smaller "rotational mass", the solid sphere is easier to rotate so the solid sphere will roll down a hill
Ex 8.** Which is easier for prying open a stuck cover from a can of paint -- a screwdriver with a thick handle or one with a long handle? Which is easier for turning stubborn screws? Why?
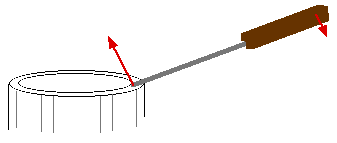
For prying open a lid from a paint can, you need a screwdriver with a long handle. The edge of the paint can provides a fulcrum or pivot or axis of rotation. The long handle provides a large lever arm as you exert a force at the end of the screwdriver handle. This means a large force is transmitted to the end of the screwdriver, which has a very small lever arm. This means a large force is supplied to the lid of the paint can.
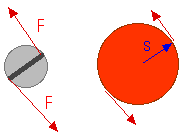
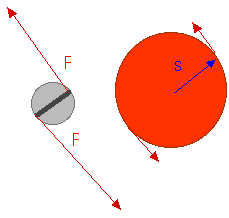
A"stubborn screw" or a "rusty screw" or a "stuck screw" needs a large "rotational force" about its axis of rotation. I have indicated that in this drawing by the forces at the edges of the screws. The length of the handle of a screwdriver has no effect on those forces or the "rotational force" they provide. But the thickness of the handle -- the diameter of the handle -- of the screwdriver does. You can only exert so much force before you hand starts to slip. But if that force is exerted on a larger-diameter handle, with a larger lever arm, the "rotational force" provided will be greater and that greater "rotational force" will be exerted on the stubborn screw.
Ex 8.** When a soaring eagle turns in its flight, what is the source of the centripetal force that acts on it?
In straight, level flight the eagle's downward weight is just balanced by the upward "lift" of the eagle's wings. As the eagle circles, his wings will change so that the "lift" has a component of force directed toward the center of the circle; this is the centripetal force.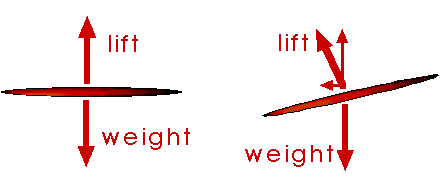
Ex 8.** Your friend says that a satellite in circular orbit does not accelerate as evidenced by its constant speed. Your other friend says it does accelerate, as evidenced by the centripetal force supplied by gravity? What do you say?
Acceleration is the time rate of change of the velocity and velocity is a vector which means it includes direction. So a change in the direction of a velocity involves an acceleration. Newton's Second Law of Motion, F = m a, tells us of the close connection between force and acceleration. Your second friend, who realizes that gravity exerts a force on the satellite, is correct in saying that force provides the mass of the satellite with an acceleration.
Pb 8.3 Hanging from one end of a light meter stick is a 1-kg weight and hanging
from the other end is a 3-kg weight. Where is the center of mass of this system
(the point of balance)? How does your answer relate to torque?

Saying "a light meter stick" just means we can ignore the mass of the meter stick itself because it is much less than even the 1-kg hanging mass.
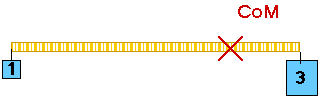
There is a center of mass (CoM) out there someplace so mark it on the diagram. We will measure distances from the CoM.
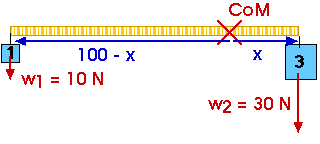
We will measure distances in centimeters (100 cm = 1 m). The 3-kg mass has a weight of 30 N (remember that w = mg) and is located at a distance of x from the CoM. The 1-kg mass has a weight of 10 N and is located at a distance of (100 - x) from teh CoM (remember, this is a meter stick so the distance between the two hanging masses must be 100 cm).
torque = (lever arm) (force) Each of these weights causes a torque. The 1-kg weight causes a counterclockwise torque about the CoM of
torque (CCW) = (100 - x) (10 N) The 3-kg weight causes a clockwise torque about the CoM of
torque (CW) = x (30 N) These two torques must be balanced,
torque (CW) = torque (CCW) x (30 N) = (100 - x) (10 N)
30 x = 1,000 - 10 x
40 x = 1,000
x = 25
x = 25 cm
Now, with the answers already in hand, it is interesting and useful to again calculate the torques about the center of mass.
torque (CW) = torque (CCW) (25 cm) (30 N) = (75 cm) (10 cm)
And we can see that the torques do, indeed, balance -- as they must.
Pb 8.5 The rock has a mass of 1 kg. What is the mass of the measuring stick if it is balanced by a support force at the one-quarter mark?
The center of mass of the measuring stick is at the one-half mark, one-quarter of the stick's length beyond the pivot.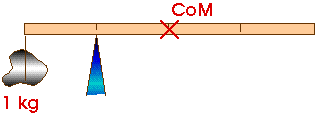
The stick is balanced by the 1-kg rock that is one-quarter of its length to the left and by its own weigh which is at the Center of Mass, one-quart of its length to the right. Therefore, the mass of the stick must be one kilogram, 1 kg.
![]()
Typical or possible multiple-choice questions:
1. Horses that move with the fastest linear speed on a merry-go-round are located
A) nearer to the centerB) nearer to the edge
C) always white
D) in front of the slower ones
2. An industrial flywheel has a greater rotational inertia when most of its mass is
A) nearer the axisB) nearer the rim
C) spread out evenly
D)
3. A cylinder and a ring roll down an incline starting at the same time. The one to reach the bottom first will be the
A) cylinderB) ring
C) neither; they both reach the bottom at the same time
D)
4. Put a pipe over the end of a wrench when trying to turn a stubborn nut on a bolt, to effectively make the wrench handle twice as long, you'll increase the torque by
A) twoB) four
C) eight
D) sixteen
5. When a twirling ice skater brings her arms inward, her rotational speed
A) increasesB) decreases
C) remains the same (or is conserved)
D)
6. To turn a stubborn screw, it is best to use a screwdriver that has a handle that is
A) long and thinB) thick or wide
C) yellow
D) slippery
7. A 1-kg rock is suspended from the tip of a meter stick at the 0- cm mark so that the meter stick balances like a see-saw when the fulcrum is at the 25-cm mark. From this information, what is the mass of the meter stick?
A) 0.25 kgB) 0.50 kg
C) 1.00 kg
D) 2.00 kg
8. A car travels in a circle with constant speed. The net force on the car is
A) directed forward, in the direction of travel.B) directed towards the center of the curve.
C) zero because the car is not accelerating.
D) directed outward, away from the center of the curve
9. One end of a long uniform log is raised to shoulder level. Another identical log is raised at its center to the same level. Raising the second log requires about
A) half as much workB) the same work
C) twice as much work
D) four times as much work
![]()
Answers to typical or possible multiple-choice questions:
1. Horses that move with the fastest linear speed on a merry-go-round are located
A) nearer to the centerB) nearer to the edge
C) always white
D) in front of the slower ones
2. An industrial flywheel has a greater rotational inertia when most of its mass is
A) nearer the axisB) nearer the rim
C) spread out evenly
D)
3. A cylinder and a ring roll down an incline starting at the same time. The one to reach the bottom first will be the
A) cylinderThe rotational mass of the ring -- with all its mass at the edge -- is I = m r2.The rotational mass of the solid disk or cylinder -- with its mass distributed throughout the cylinder or disk -- is I = (1/2) m r2.
That is, the cylinder has a smaller rotational mass. That means it -- the cylinder -- will win; it will roll down the inclined plane faster and reach the bottom first.
B) ring
C) neither; they both reach the bottom at the same time
D)
4. Put a pipe over the end of a wrench when trying to turn a stubborn nut on a bolt, to effectively make the wrench handle twice as long, you'll increase the torque by
A) twotorque = rotational force = force x lever armIf we make the lever arm twice as great, we increase the torque by two.
B) four
C) eight
D) sixteen
5. When a twirling ice skater brings her arms inward, her rotational speed
A) increasesangular momentum = constantangular momentum = angular momentum
(rotational mass) x (rotational speed) =
= (rotational mass) x (rotational speed)B) decreases
C) remains the same (or is conserved)
D)
6. To turn a stubborn screw, it is best to use a screwdriver that has a handle that is
A) long and thinB) thick or wide
torque = rotational force = force x lever armC) yellow
D) slippery
7. A 1-kg rock is suspended from the tip of a meter stick at the 0- cm mark so that the meter stick balances like a see-saw when the fulcrum is at the 25-cm mark. From this information, what is the mass of the meter stick?
A) 0.25 kgB) 0.50 kg
C) 1.00 kg
A diagram helps here; see the homework, Pb 8.3 .D) 2.00 kg
8. A car travels in a circle with constant speed. The net force on the car is
A) directed forward, in the direction of travel.B) directed towards the center of the curve.
This net force is called the "centripetal force".C) zero because the car is not accelerating.
D) directed outward, away from the center of the curve
9. One end of a long uniform log is raised to shoulder level. Another identical log is raised at its center to the same level. Raising the second log requires about
A) half as much workB) the same work
C) twice as much work
Lifting the end of the log to shoulder height only lifts the center of mass to half that height. Lifting the center of the second log to shoulder height lifts the center of mass to full shoulder height so twice the work is required.D) four times as much work
| Back to Calendar | ToC, Ch 8 | Ch 9, Gravity |
(C) 2003, Doug Davis; all rights reserved