
Enter all your answers in the “Scantron
sheet” or the “bubble sheet” or the “answer
sheet”. Turn in only that sheet. Anything you
write on this exam will not be seen or
used or considered or graded. Be sure your name is on the
“bubble sheet” you hand in. Be sure your name is
bubbled-in. Be sure your answers are recorded correctly. Please put
the date on the sheet as well.
For every question, also consider the following as a
possible answer:
E) none of the above
Possibly useful information:

For every question, also consider the following as a possible answer:
e) none of the above
1. Electromagnetic waves consist of
a) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses.
b) oscillating electric and magnetic
fields.
c) particles of light energy.
d) high-frequency gravitational waves.
2. Electromagnetic waves
a) can travel through a vacuum.
b) need a medium to travel through.
3. The main difference between a radio wave and a light wave
is its
a) speed
b) wavelength
c) EM characteristic
d) all of the above
4. Which of these electromagnetic waves has the
shortest wavelength?
a) X-rays
b) ultraviolet waves
c) infrared waves
d) radio waves
5. Compared to ultraviolet waves, the wavelength of infrared
is
a) longer
b) identical
c) shorter
6. Compared to radio waves, the velocity of visible light
waves in a vacuum is
a) greater
b) the same
c) less
7. Compared to radio waves, the wavelength of visible light
waves in a vacuum is
a) longer
b) the same
c) shorter
8. Which of the following is fundamentally different from the
others?
a) X-rays
b) visible light waves
c) sound waves
d) radio waves
9. The sensation of color is seen when light falls on the
eye's
a) rods
b) cones
c) cornea
d) crystalline lens
10. The cones in the retina of the eye are
a) most densely packed at the center of
vision, the fovea.
b) uniformly spread along the visual field.
c) concentrated along the periphery of vision.
d) concentrated at the “blind spot” where the optic nerve
attaches to the retina.
11. If a light signal and a radio signal were emitted
simultaneously from Alpha Centauri, the star closest to Earth,
the first signal to reach Earth would be the
a) the radio signal.
b) the light signal.
c) both would arrive at the same
time.
12. Color depends on what characteristic of light?
a) wavelength
b) frequency
c) both of these
d) neither of these
13. The colored dots that make up the color on a TV screen
are
a) red, yellow, green.
b) red, yellow, blue.
c) red, green, blue.
d) cyan, magenta, yellow.
14. Magenta light is a mixture of
a) red and yellow.
b) cyan and yellow.
c) red and blue.
d) yellow and blue.
15. Colors seen on TV result from color
a) subtraction.
b) addition.
c) neither of these.
d) either of these.
16. Colors seen on the cover of a magazine result from
color
a) subtraction.
b) addition.
c) neither of these.
d) either of these.
17. Different colors of light correspond to different
light
a) velocities.
b) intensities.
c) polarities.
d) frequencies.
18. Look at a full-color picture in a magazine with a
magnifying glass and you'll see that the inks used are
a) red, green, cyan, and blue.
b) red, green, blue, and black.
c) magenta, cyan, yellow, and
black.
d) magenta, cyan, yellow, and blue.
19. A sheet of red paper will look black (or dark grey)
when illuminated with
a) red light.
b) cyan light.
c) yellow light.
d) magenta light.
20. A blue object will appear black (or dark grey) when
illuminated with
a) blue light
b) yellow light --> changed to "green light"
c) red light
d) cyan light
21. A mixture of red and green light produces
a) blue.
b) magenta.
c) yellow.
d) cyan.
22. A spotlight produces white light which then passes through
a filter that absorbs the yellow light. What color is the light that
passes through?
a) red.
b) green.
c) blue.
d) yellow.
23. A spotlight produces white light which then passes through
a filter that absorbs the red light. What color is the light that
passes through?
a) red.
b) yellow.
c) magenta.
d) cyan.
24. Light travels fastest in
a) water.
b) vacuum.
c) air.
d) glass.
25. Refraction, as light goes from air to glass, results from
differences in light's
a) frequency in air and glass.
b) incident angle.
c) speed in air and glass.
d) all of the above.
26. Light refracts when traveling from air into glass because
light
a) intensity is greater in air than in glass.
b) frequency is greater in glass than in air.
c) speed is greater in air than in
glass.
d) polarization is greater in glass than in air.
27. A beam of light emerges from water into air at an angle.
The beam is bent
a) toward the normal.
b) away from the normal
c) at an angle of 49° .
d) only if it is polarized.
28. When a light beam emerges from water into air, the light
speed
a) increases.
b) remains the same.
c) decreases.
29. Refraction causes the bottom of a swimming pool to
appear
a) farther away than it really is.
b) closer to the surface than it really
is.
30. Different colors are dispersed by a prism because
different colors in the prism have different
a) speeds.
b) directions.
c) energies.
d) momenta.
31. The critical angle for a transparent material is the angle
at and beyond which all light within the material is totally
a) absorbed.
b) reflected.
c) refracted.
d) polarized.
32. In an optical fiber, light actually
a) curves in a direction parallel to the central axis of the
fiber.
b) travels in straight-line
segments.
c) travels along the outer surface of the fiber.
d) all of the above.
33. Your image in a plane mirror is
a) virtual.
b) real.
c) both of these.
34. The type of lens that spreads parallel light is a
a) converging lens.
b) diverging lens.
c) either of these.
35. Which of the following can be projected onto a viewing
screen?
a) a virtual image.
b) a real image.
c) a convex image.
d) a concave image.
36. The image of something “infinitely far away”,
like the Sun, produced by a converging lens appears
a) between the lens and the focal point.
b) at the focal point.
c) between the focal point and twice the focal length.
d) at twice the focal length.
37. Your vision is sharpest when your pupil is
a) dilated or opened wide.
b) constricted or made tiny.
c) blue
d) brown
38. According to Huygens' principle, every point on a wave
a) is a diffraction source.
b) behaves as a source of new
waves.
c) is the superposition of every other part of the wave.
d) all of the above.
39. Consider plane waves incident upon a barrier with a small
opening. After passing through the opening, the waves
a) continue as plane waves.
b) spread out.
c) are polarized.
d) converge.
40. Light will not pass through a pair of Polaroids when their
axes are
a) parallel.
b) rotated 45°.
c) rotated 57°.
d) perpendicular.
41. Monochromatic light is light of a single
a) color
b) wavelength
c) frequency
d) all of the above
42. Light from a laser is
a) monochromatic.
b) in phase.
c) coherent.
d) all of the above.
43. A 2-m tall person viewing his full-length image in a plane
mirror requires a mirror that is at least
a) 0.5 m
b) 1.0 m.
c) 2.0 m.
d) This depends upon how far the person is from the mirror.
44. In the interference pattern produced by shining a laser
through two slits (Young’s double slit experiment), the bright
areas are the result of
a) destructive interference.
b) polarization.
c) constructive interference.
d) restructive construction.
45. When light passes through a diffraction grating it is
bent. Light with a greater wavelength will be bent
a) through a smaller angle.
b) the same (bending is independent of wavelength).
c) through a larger angle.
46. Rainbows are a result of
a) dispersion and reflection.
b) dispersion and polarization.
c) reconstruction and polarization.
d) constructive and destructive interference.
47. An object is placed 20 cm from a converging lens that has
a focal length of 10 cm. Make a ray diagram of this situation. From
the ray diagram, characterize the image.


The image is
a) real, and inverted.
b) virtual, inverted, and smaller.
c) virtual, upright, and smaller.
d) virtual, inverted, and larger.
48. An object is placed 30 cm from a converging lens that has
a focal length of 10 cm. Make a ray diagram of this situation. From
the ray diagram, characterize the image.


The image is
a) real, inverted, and larger.
b) real, inverted, and
smaller.
c) virtual, upright, and smaller.
d) virtual, inverted, and smaller.
49. An object is placed 15 cm from a converging lens that has a
focal length of 10 cm. Make a ray diagram of this situation. From the
ray diagram, characterize the image.


The image is
a) real, inverted, and
larger.
b) real, inverted, and smaller.
c) real, upright, and smaller.
d) virtual, upright, and larger.
50. An object is placed 5 cm from a converging lens that has a
focal length of 10 cm. Make a ray diagram of this situation. From the
ray diagram, characterize the image.

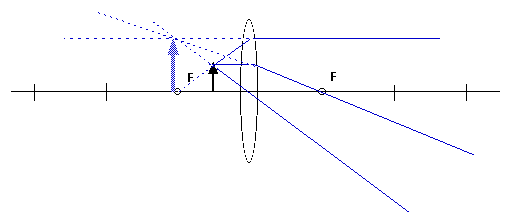
The image is
a) real, inverted, and larger.
b) real, inverted, and smaller.
c) virtual, upright, and smaller.
d) virtual, upright, and
larger
Here are two more ray diagrams.
*. An object is placed 30 cm from a diverging lens that has
a focal length of - 10 cm. Make a ray diagram of this
situation. From the ray diagram, characterize the image.


The image is
A) real, inverted, and larger.
B) real, inverted, and smaller.
C) virtual, upright, and
smaller.
D) virtual, inverted, and smaller.
*. An object is placed 20 cm from a concave mirror that has a
focal length of + 30 cm. Make a ray diagram of this situation.
From the ray diagram, characterize the image.


The image is
A) real, inverted, and larger.
B) real, inverted, and smaller.
C) virtual, upright, and
larger.
D) virtual, inverted, and smaller.